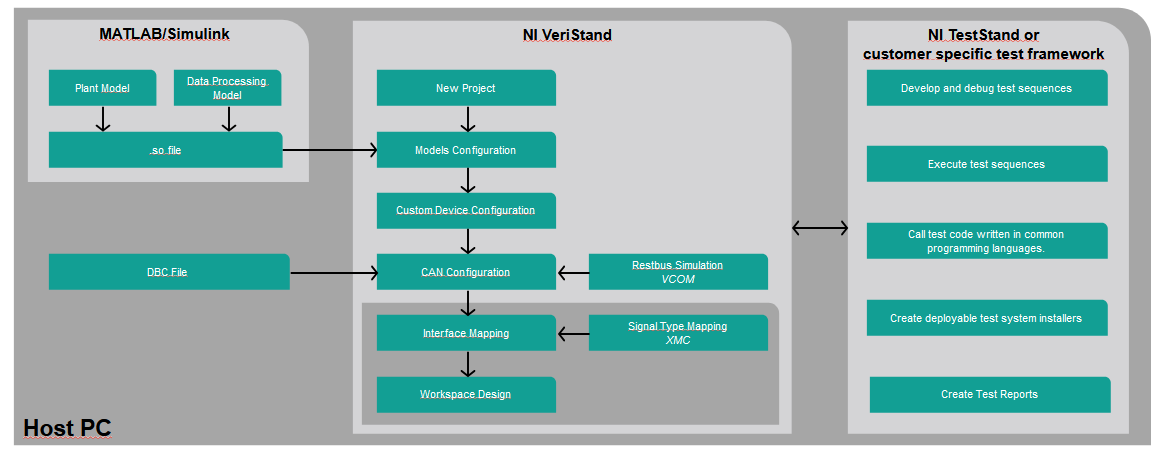
Interoperability and Market Overview
Different HIL vendors. Each with their own value. Important to consider how to integrate legacy system with new systems. Maximize re-use. NI has aimed to as modular and interoperable as possible, as the complexity of HIL systems has expanded this flexibility to a test engineer. On the NI platform multiple approaches include the following.
- Co-simulation
- As each HIL vendor has their own strengths it can be preferential to implement a co-simulation. This may where components of the simulation are on a distributed system, or alternative HIL platform. This can be leveraged to improve re-use of established workflows or leverage capabilities from a wider range of technology suppliers.
- Model conversion
- In most, if not all cases, for modern HIL systems there is a requirement to leverage models built earlier in the design cycle. In most organisations it is fair to assume that these teams would use a range of software platforms. It can then often be time consuming and costly when for validation these models need to be recompiled or rebuilt. To support these workflows NI works directly with a wide range of simulation partners to make available tools that can automatically compile a model for our platform. This technology has extended to where NI is now able to convert a model previously built for other HIL vendors to work with the NI platform.
- Model import
- NI’s modularity in hardware is extended to the modularity in software, As such when working on the NI platform models are contained as individual parallel processes. Which means we are able to import and deploy onto a single RT target multiple models from differing vendors. This also means that when updating your HIL simulation we are able to update only specific sub components rather than the whole HIL simulation.