webvi-examples
Call 3rd Party Web Service
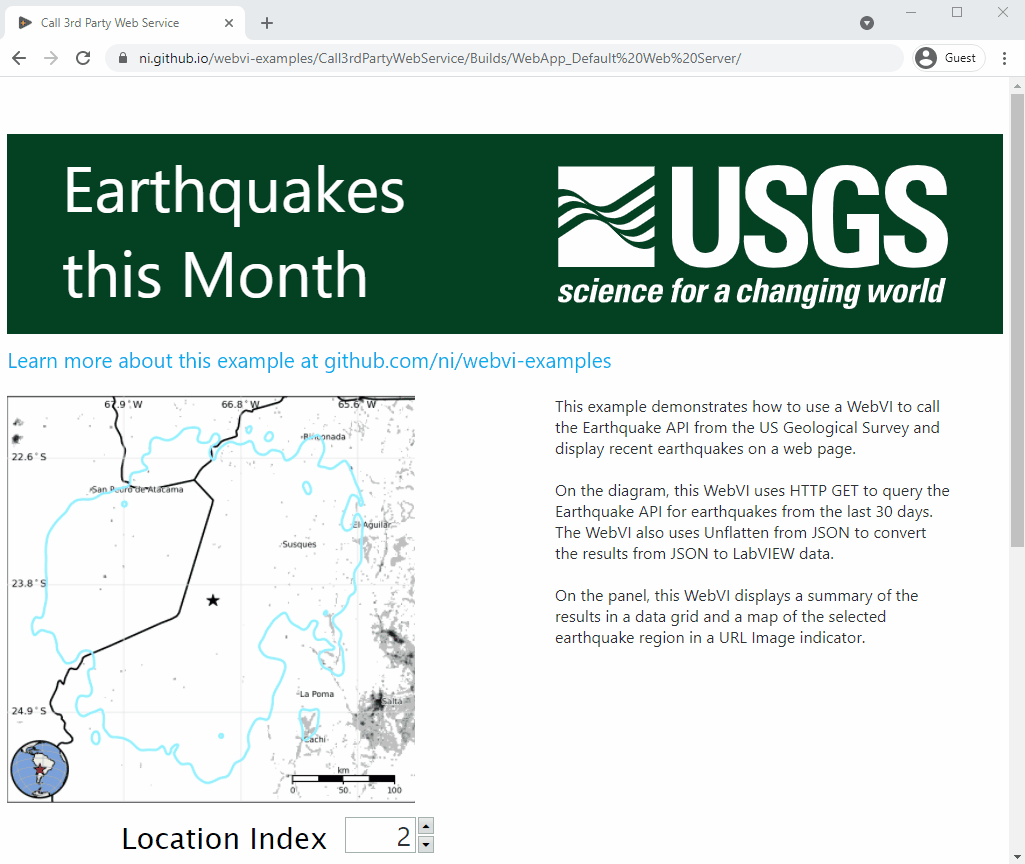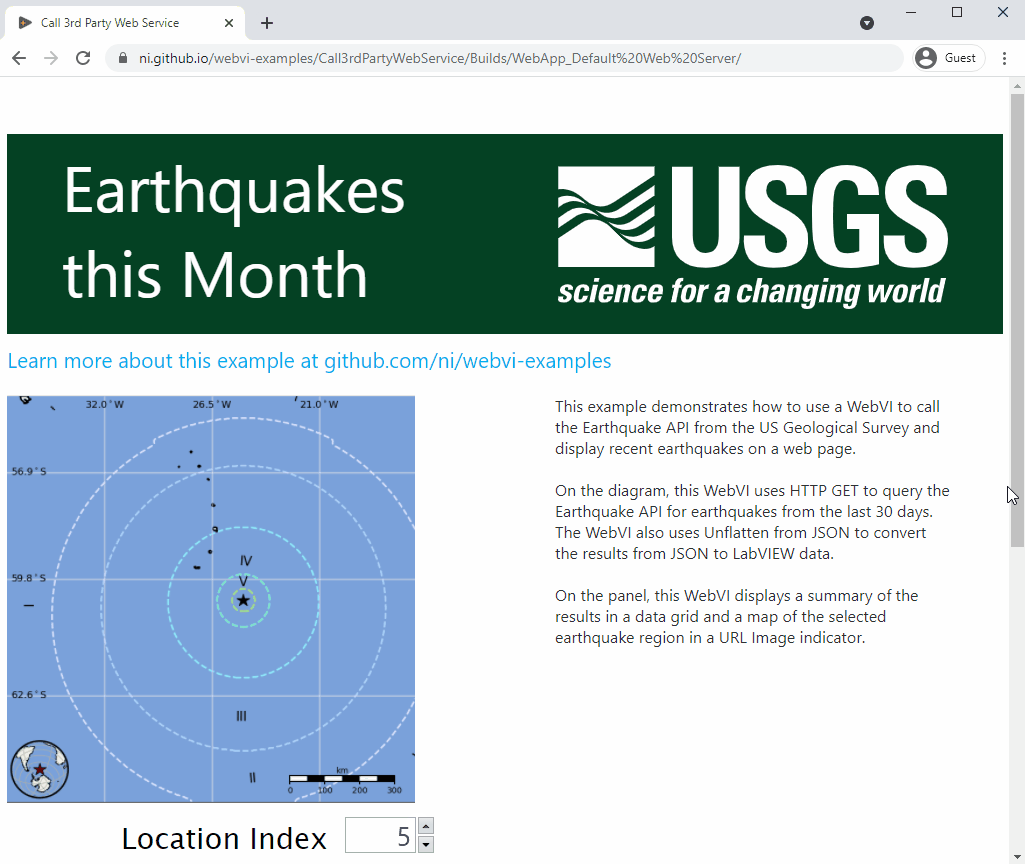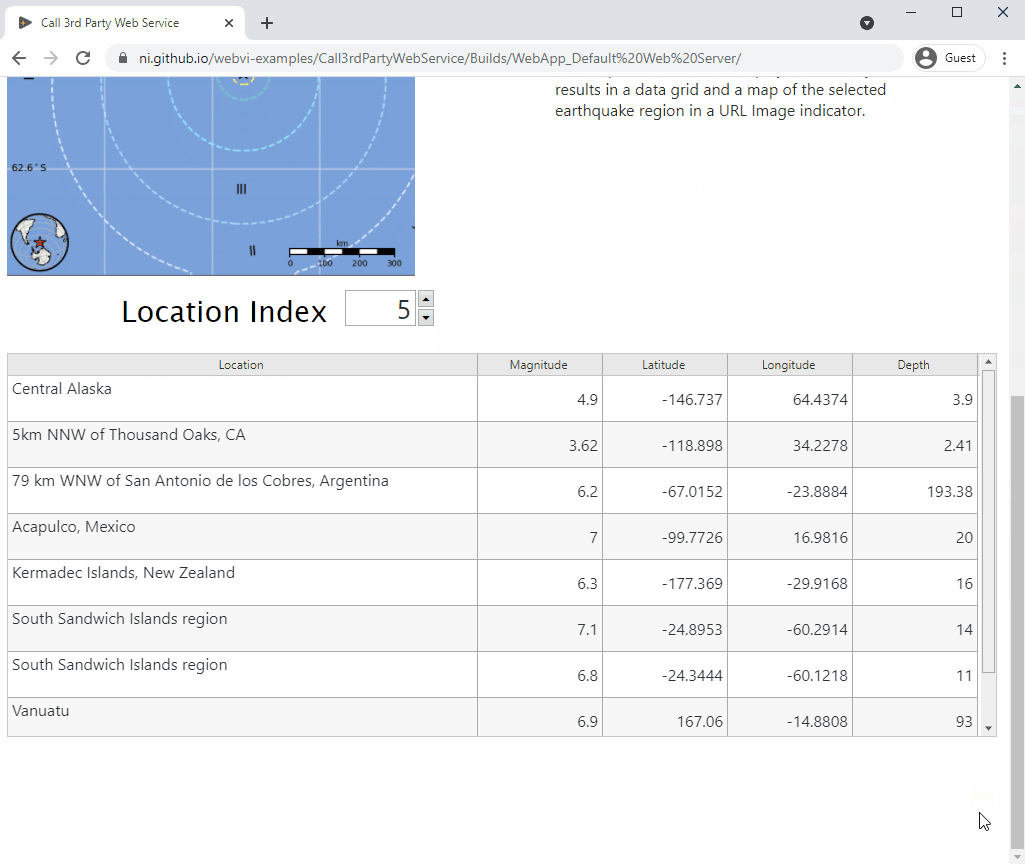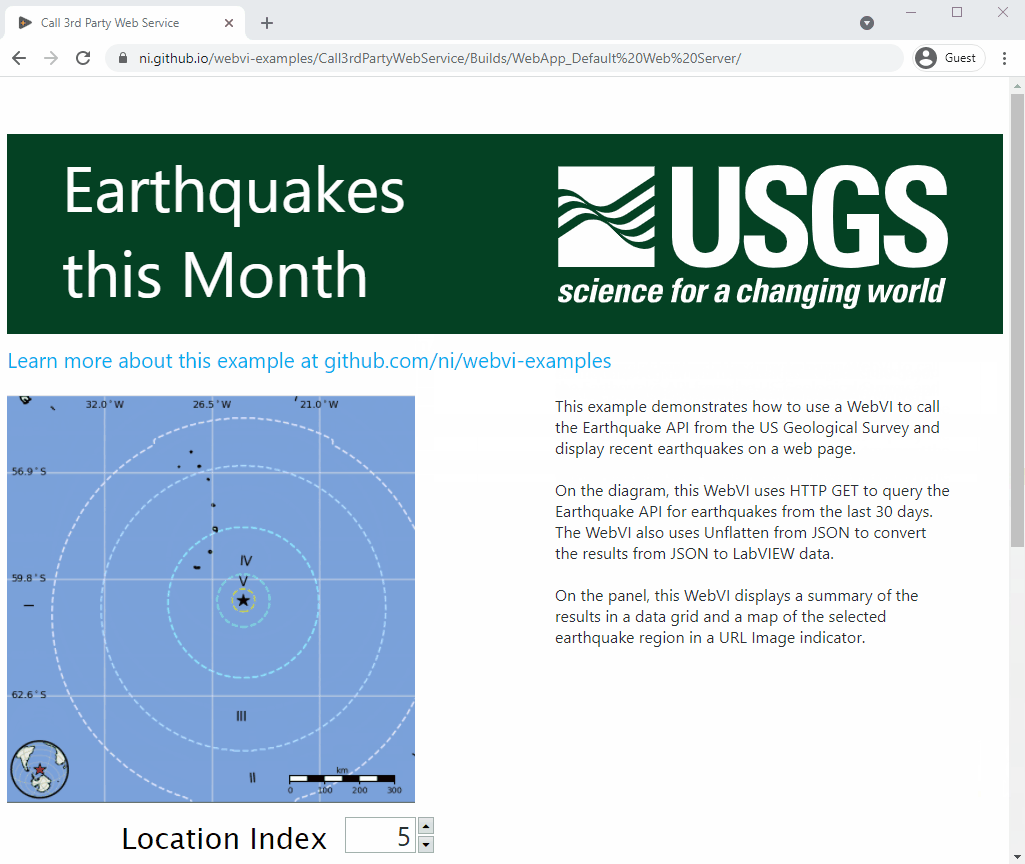
This example demonstrates how to use a WebVI to call the Earthquake API from the US Geological Survey and display recent earthquakes on a web page.
On the diagram, this WebVI uses HTTP GET to query the Earthquake API for earthquakes from the last 30 days. The WebVI also uses Unflatten from JSON to convert the results from JSON to LabVIEW data.
On the panel, this WebVI displays a summary of the results in a data grid and a map of the selected earthquake region in a URL Image indicator.
Dependencies
- G Web Development Software
Setup
- Clone the ni/webvi-examples repository to your machine.
- Open
Call3rdPartyWebService/Call3rdPartyWebService.gwebproject - Open
index.gviweband click the Run button. - Build the web application.
a. OpenWebApp.gcomp.
b. On the Document tab, click Build.- To view the build output on your machine, click Output Directory on the Document tab once your application finishes building.
- To launch and view the Web Application locally you can use the Run button on the Document tab.
Hosting
You can manually the move the build output found at \Call3rdPartyWebService\Builds to any web server. This project also includes a Distribution (WebApp.lvdist) that can be used to build a package (.nipkg). Packages utilize NI Package Manager to automated the process of installing, upgrading, or removing the web app. A package is also a requirement for hosting a Web application on SystemLink Cloud.
SystemLink Cloud Web App Hosting
The following steps can be used to host the web app on SystemLink Cloud
- Open
Call3rdPartyWebService.gwebproject. - Open
WebApp.lvdist. - Click the build icon in the top command bar of this distribution document
- Open a Web browser and navigate to https://www.systemlinkcloud.com/webapphosting
- Click the Choose nipkg button and select the nipkg built in step 3.
- When the upload is complete, click on your newly uploaded Web app from your list of Web apps
Local Hosting
The following steps can be used to host the web app on a local web server
Hosting on the NI Web Server with a nipkg
- Open
Call3rdPartyWebService.gwebproject - Open
WebApp.lvdist. - Click the build icon in the top command bar of this distribution document
- Double-click the nipkg and follow the on screen instructions
- Open a web browser and navigate to
http://localhost:9090/call3rdpartywebservice/
Hosting on the NI Web Server by manually moving files
- Open
C:\Program Files\National Instruments\Shared\Web Server\htdocs - Copy the
WebApp_Default Web Serverdirectory into thehtdocsdirectory - Open a web browser and navigate to
http://localhost:9090/WebApp_Default%20Web%20Server/
Hosting on the LabVIEW 2009-2021 Web Server
- Open
C:\Program Files (x86)\National Instruments\Shared\NI WebServer\www - Copy the
WebApp_Default Web Serverdirectory into thewwwdirectory - Open a web browser and navigate to
http://localhost:8080/WebApp_Default%20Web%20Server/
Details
A web service is a collection of functions that can be called through the web to trigger behavior or return data. Many websites offer these APIs as a way for third-party developers to build new applications using the website’s underlying data or functionality.
Many web services are open and public like the Earthquake API. Others require registration and API keys that restrict access to specific users and limit the load on the service.
To call a web service in a WebVI, this example uses the HTTP Get node to pass in the URL of the service and return a string with the result of the call. There are examples of this in several WebVIs, including GetRecentEarthquakes.gviweb.
Web services return data in a variety of formats, such as JSON, XML, CSV, and YML. The USGS Earthquake service returns JSON, which LabVIEW can parse using the Unflatten from JSON node. To use Unflatten from JSON, you must specify the structure the data is expected to take and can provide a path to limit the search to a specific part of the data. There are examples of this in several WebVIs, including Get Earthquake Count.gviweb.
If the web service returns data in a format other than JSON, you can still parse it in the WebVI using String nodes. There is an example of this in Get Map URL.gviweb.
Once the data has been retrieved and converted into LabVIEW data types, this example displays the data in indicators on the panel of the top-level WebVI, index.gviweb. This example uses a data grid to show all earthquakes and a URL Image indicator to display a map of the surrounding area.

